José Guadalupe Posada, born in early 1852 in the state of Aguascalientes, Mexico, developed his skill as an artist into a career as the foremost political cartoonist of his era, regularly skewering the high and mighty of late 19th century Mexico with his engravings. His portrait (above), engraved by mid-20th century engraver Leopoldo Méndez, is a classic.
Posada's satirical efforts started when he worked as a teenage apprentice in Aguascalientes. His boss, José Trinidad Pedroza, assigned him the job of creating a finger-pointing cartoon depicting the misdeeds of a local politician. His characterization was so successful that it created a tremendous hullabaloo in Aguascalientes; both Posada and Pedroza had to leave town in a hurry to avoid the politico's wrath. When the tumult calmed down, the two printers returned to their work of exposing nefarious political goings-on.

Posada, photographed around the turn of the 20th century, standing in the doorway of his Mexico City taller de grabado (engraving workshop).
When Pedroza's Aguascalientes workplace was destroyed by a flood in 1888, Posada moved to Mexico City to open his own workshop. After the move to the capital, Posada began publishing and distributing frequent volantes (flyers). He used the medium to continue to puncture the egos and expose the foibles and serious crimes of government and social figures of the day. During a time when many in Mexico were illiterate, the message of political cartoons could be easily understood even without reading the articles. Many credit Posada with raising the political and social consciousness of the peón (common laborer), exposing social injustice at a time when most at that level were blind to it.

Posada's first published fashionably-hatted calavera (skull). The cartoon is titled, "Big Sale of Grinning Skulls". Over the course of the rest of his career, it is estimated that the prolific Posada published as many as 20,000 political volantes, at a penny apiece, including many thousands that were illustrated by calaveras.
What was Posada's purpose in utilizing a skeleton–albeit a well-dressed skeleton–to illustrate his articles? Mexico's president/dictator at the time, Porfirio Díaz, appreciated and aped all things French. During his rule, known as the Porfiriato, Mexican government officials and high society alike dressed in the French mode, expressing what was known then and is known now as malinchismo: over-valuing foreign imports over Mexico's national products. The Frenchified calavera engraved by Posada is offered as a satirical portrait of those Mexican natives who, Posada felt, were aspiring to adopt European aristocratic traditions in Mexico's pre-revolutionary era. The irony of Posada’s drawing—a fabulously over-dressed skeleton—is that no matter what we’re wearing, we all end as bones.

El Jarabe en Ultratumba (Dancing Beyond the Grave).
In Mexico, we play with, make fun of, and party with death. We throw our arms around her in a wickedly sardonic embrace and escape her return embrace with a zippy side-step, a wink, and a joke. Every day is a dance with death. Death is a woman who has a numerous affectionate and humorous nicknames: la Huesuda (the bony woman), la Seria (the serious woman), la Novia Fiel (the faithful bride), la Igualadora (the equalizer), la Dientona (the toothy woman), la Pelona (the bald woman), la Patrona (the boss lady), and a hundred more. She's always here, just around the next corner or right over there, behind that pillar. She waits with patience, until later today or until twelve o'clock next Thursday, or sometime next year–but when it's time, she's right there to dance away with you at her side.

In the fairly recent past, Posada's politicized calavera became known as la catrina, a figure now closely related to Mexico's celebration of Día de los Muertos (Day of the Dead). Renowned Michoacán-based painter and sculptor Juan Torres Calderón, Mexico Cooks! good friend, was the first to present Posada's catrina vision in clay. In 1982, his wife, Velia Canals, began production of Maestro Torres' catrina designs. Their workshop in Capula, Michoacán, is open for sales to the public.
The Mexican word catrina–the word now used for any representation of Posada's original French-attired calavera–simply means a woman who is dressed to the nines. Her male counterpart is known as a catrín—a handsome man, usually dressed in elegant male attire. Together, the couple are catrines. Even today, if you go out to a formal event, your neighbor (seeing you leave the house) might well say, “Uff, qué catrina!” Unless you’re a man, of course, in which case the neighbor would say, “Qué catrín!”.

These catrines are made of paper maché. On the far right, you see a bride and groom. Mexico Cooks!' kitchen shows off this same artisan's chef figure, in a green chef's jacket and a high white toque. Enlarge any photo to have a better view.

Some of the many Día de los Muertos figures displayed at the fabulous bakery Hornos de Los Ortíz, in Morelia, Michoacán. The owner makes these gorgeous figures out of bread dough! If you happen to be in Morelia in the next few weeks, DO NOT MISS this bakery and its annual display. The owners, in a typical Mexican play on words, call the diorama a pan-teón: bread cemetery.

During the 2015 Noche de los Muertos events in Morelia's historic center, this young woman dressed in a skirt and hat made of totomoxtle (dried corn husks)–the husks normally used for making tamales. Her mother made her outfit and painted her face.
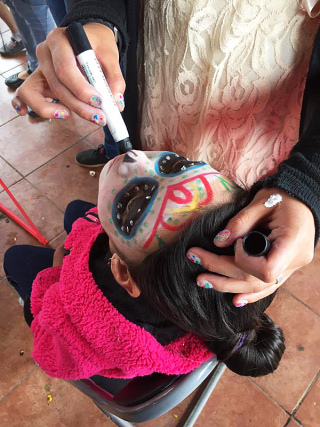
During the last few years, many Mexican children and adults have begun to paint their faces for Día (and Noche) de Muertos. The little girl in the chair lives in Opopeo, Michoacán, a small town not far from Morelia. In the town square's bandstand, young people were designing a special face for each child who wanted one.
Posada's century-old political calavera has evolved into one of Mexico's most beloved icons, the catrina. When your friends ask you about her, be sure that they know the history behind this beautiful creature. She's more than just a pretty face.
Looking for a tailored-to-your-interests specialized tour in Mexico? Click here to see new information: Tours